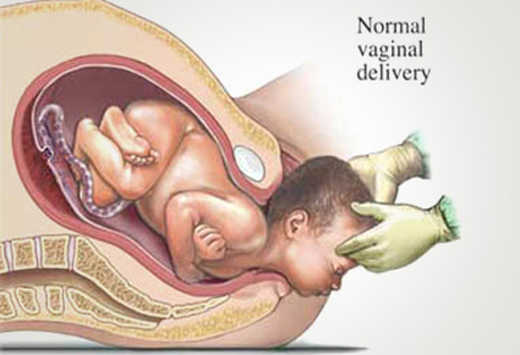
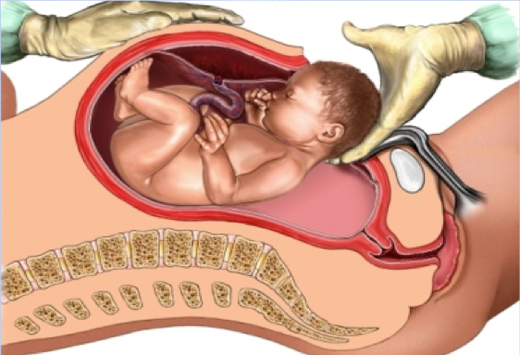
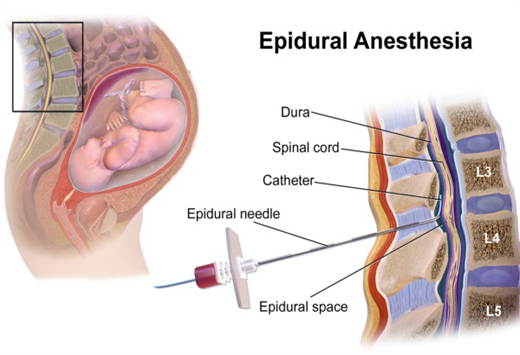
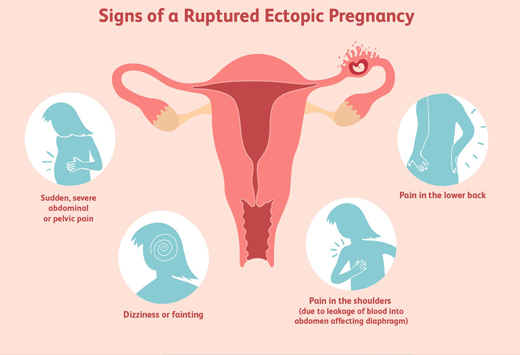
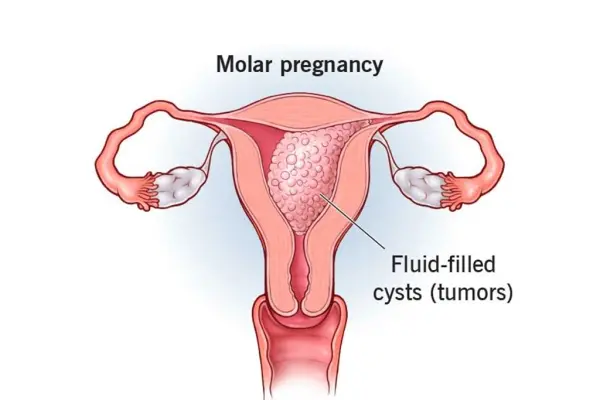
What is MATERNITY CARE??
Maternity care is the medical care a woman receives during pregnancy, childbirth, and after giving birth. It includes regular check-ups with a doctor or midwife to monitor the health of the mom and baby. The goal is to ensure a healthy pregnancy, safe delivery, and a healthy baby. Maternity care also includes education on pregnancy, childbirth, and caring for a newborn. It may include tests and screenings to detect any potential problems early on. Maternity care providers offer support and guidance throughout the pregnancy journey. They help women make informed decisions about their care and birth plan. Maternity care also includes care after the baby is born, like postpartum check-ups and breastfeeding support. It's an essential part of having a healthy and happy pregnancy and baby. Maternity care is usually provided by obstetricians, midwives, and other healthcare professionals.