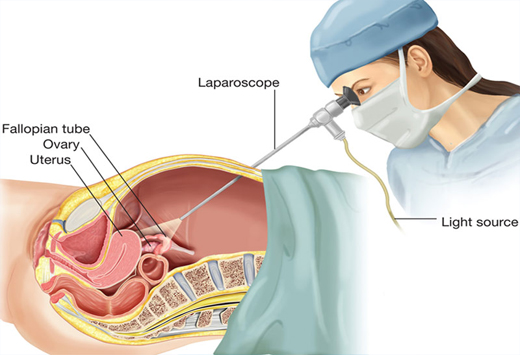
What is a LAPAROSCOPY AND HYSTEROSCOPY
(દુરબીન થી થતા ઓપરેશન)??
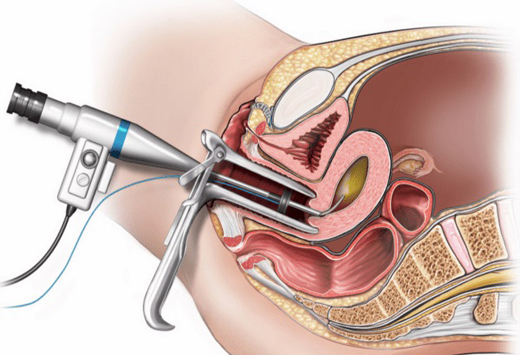
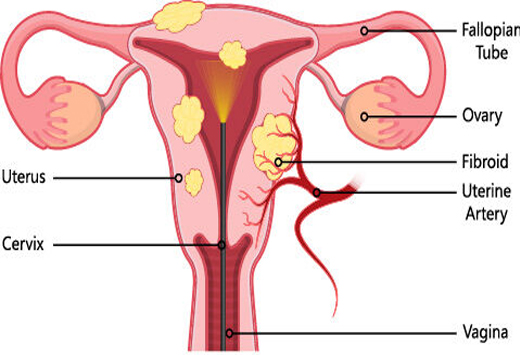
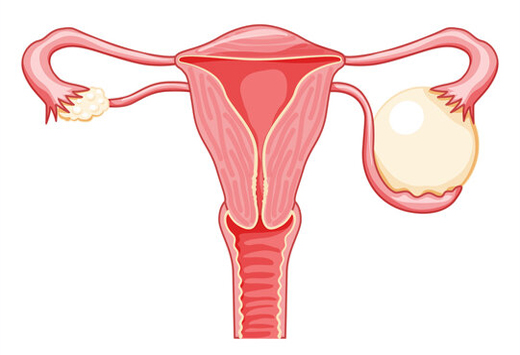
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy, are both minimally invasive surgical procedures used to diagnose and treat certain medical conditions related to the reproductive organs. Laparoscopy involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached (laparoscope) is inserted. This allows doctors to view the pelvic organs such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes on a monitor. It's commonly used to diagnose conditions like endometriosis, ovarian cysts, or to evaluate infertility causes. Hysteroscopy, on the other hand, involves inserting a thin, lighted telescope-like device (hysteroscope) through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. It helps doctors examine the inside of the uterus for abnormalities like fibroids, polyps, or adhesions. Additionally, it can be used to perform certain surgical procedures like removing polyps or fibroids. Both procedures are performed under general anesthesia and offer advantages such as shorter recovery times, less pain, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery. They play crucial roles in diagnosing and treating various gynecological conditions while minimizing discomfort and recovery time for patients.